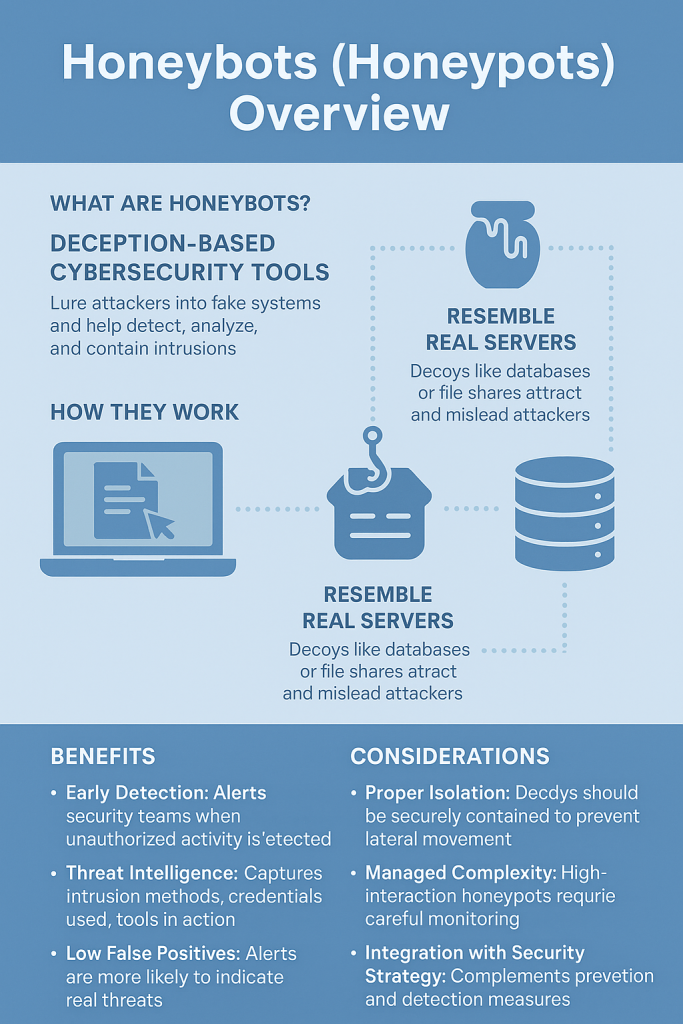
What Are Honeybots?
Honeybots—also known as honeypots—are deception-based cybersecurity tools designed to lure attackers into fake, decoy systems that resemble genuine network assets. They help organizations detect, analyze, and contain intrusions while protecting actual infrastructure.
How They Work
Honeybots mimic real servers—such as databases, file shares, or network devices—to entice cybercriminals into engaging with what they believe is genuine infrastructure. These decoys act as early warning systems and provide intelligence on attacker behavior.
Some platforms enhance this approach by using real server-based honeypots deployed through dual-layer virtualization, ensuring attackers are contained and prevented from moving into production environments.
Benefits
Early Detection: Alerts security teams when unauthorized activity is detected, often before it reaches real assets.
Threat Intelligence: Captures details such as intrusion methods, credentials used, and tools in action.
Low False Positives: Since genuine users do not interact with honeypots, alerts generated are highly meaningful.
Scalable Deployment: Supports multiple honeypot types (e.g., MySQL, SMB, SSH) with minimal resource usage.
Considerations
Proper Isolation: Decoys should be securely contained to prevent attackers from using them as a pivot point.
Managed Complexity: High-interaction honeypots can yield more insights but require careful monitoring and configuration.
Integration with Security Strategy: Honeypots should complement other detection and prevention measures for a layered defense.